Research
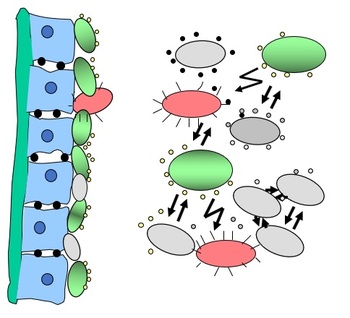
Bacteria as single living organisms are exposed to rapidly changing external conditions. Given strong selection pressure, it is not surprising that bacteria have evolved sophisticated signaling systems to constantly monitor changes in external parameters, such as acidity, nutrients, eukaryotic signals and to adapt their structure, physiology and behavior accordingly.
Research in Kirsten Jung's lab focuses on elucidating the molecular mechanisms of stimulus perception under acid stress in Escherichia coli and other γ-proteobacteria (Area 1). We study the uptake, excretion and homeostasis of primary metabolites, such as pyruvate, in Escherichia, Salmonella and Vibrio (Area 2). We elucidate the role of RNA modifications during abiotic and biotic stress response in Escherichia and Vibrio(Area 3). We also investigate translation elongation factor P (EF-P), a protein that alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches, and its post-translational modification systems (Area 4). Last but not least, we are working on identifying new intracellular targets of natural compounds (Area 5).
Area 1
Acid stress sensing in Escherichia coli and other γ-proteobacteria
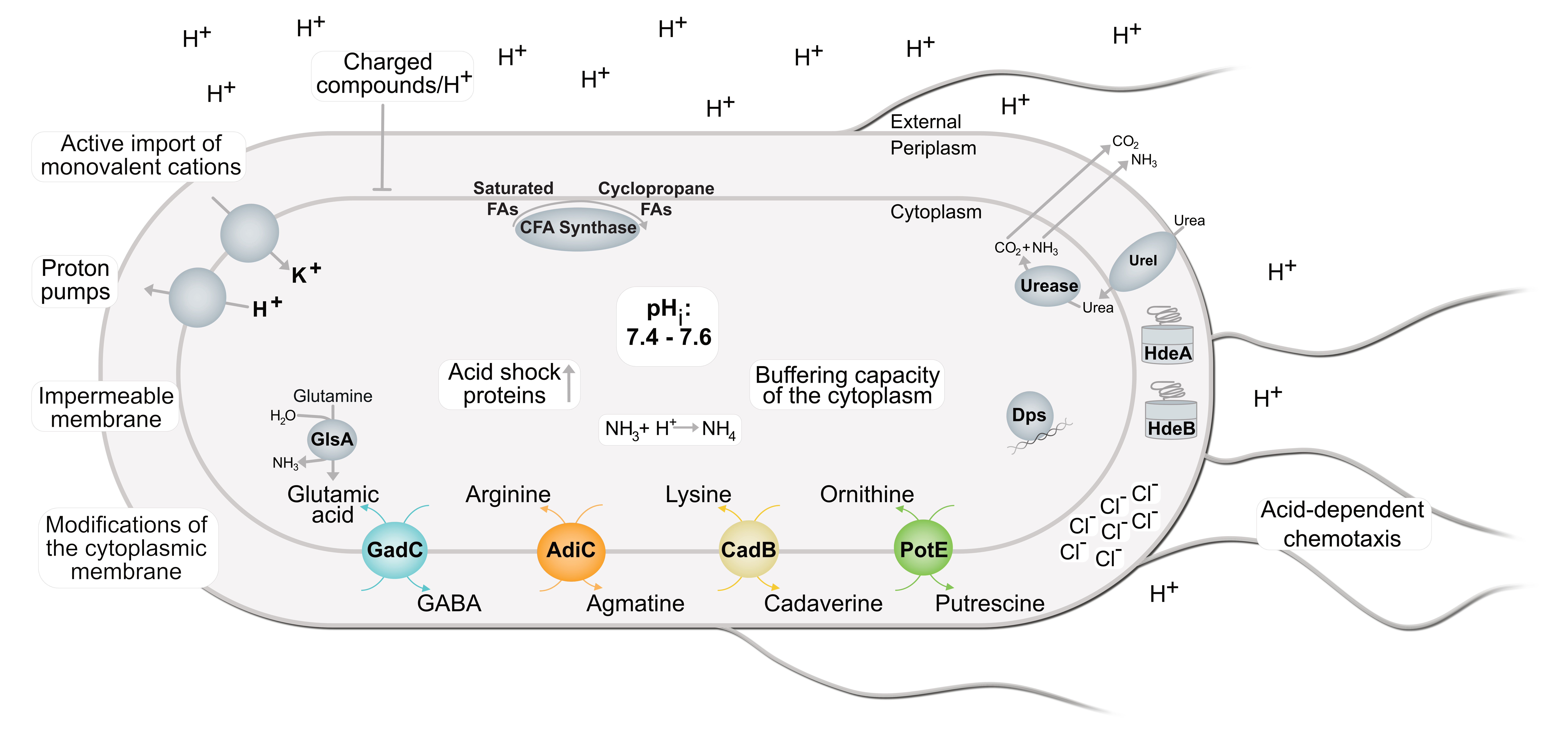
Acid resistance is an important property of many bacteria to survive in acidic environments like the human gastrointestinal tract. E. coli, for example, has several sophisticated signaling systems to sense and appropriately respond to environmental acid stress by regulating the activity of five inducible acid resistance systems. We investigate how Gram-negative bacteria sense environmental acidity using membrane-integrated and cytosolic pH sensors.
Selected Publications:
- Schumacher, K., Gelhausen, R., Backofen, R., Kion-Crosby, W., Barquist, L., Jung, K. (2023) Ribosome profiling reveals the fine-tuned response of Escherichia coli to acid stress. mSystems, Nov 1:e0103723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01037-23
- Schwarz, J., Brameyer, S., Hoyer, E., Jung, K. (2023) The interplay of AphB and CadC to activate acid resistance of Vibrio campbellii. J. Bacteriol., 205: e0045722. doi: 10.1128/jb.00457-22.
- Brameyer, S., Schumacher, K., Kuppermann, S., Jung, K. (2022) Division of labor and collective functionality in Escherichia coli under acid stress. Commun. Biol., 5: 327.
- Martini, L., Brameyer, S., Hoyer. E., Jung. K.*, Gerland, U.* (2021) Dynamics of chromosomal target search by a membrane-integrated one-component receptor. PloS Comp. Biol., 17: e1008680.
- Brameyer, S., Hoyer, E., Bibinger, S., Burdack, K., Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2020) Molecular design of a signaling system influences noise in protein abundance under acid stress in different gamma-proteobacteria. J. Bacteriol., 202(16): e00121-20.
- Brameyer, S., Rösch, T.C., Andarib, J.A., Hoyer, E., Schwarz, J., Graumann, P.L., Jung, K. (2019) DNA-binding directs the localization of a membrane-integrated receptor of the ToxR family. Commun. Biol., 2:4.
- Fritz, G., Koller, C., Tetsch, L., Haneburger, I., Burdack, K., Jung, K., Gerland, U. (2009) Induction kinetics and feedback inhibition of a conditional stress response system in Escherichia coli, J. Mol. Biol. 393: 272–286.
- Schumacher, K., Brameyer, S., Jung, K. (2023) Bacterial acid stress response: from cellular changes to antibiotic tolerance and phenotypic heterogeneity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 75: 102367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2023.102367
Area 2
Molecular mechanisms of stimulus perception by histidine kinase/response regulator systems and regulation of uptake and excretion of primary metabolites
Bacteria sense and respond to various stress conditions by employing so called two-component systems. These systems consist of a histidine kinase and a response regulator, which sense environmental stimuli, transduce information via phosphorylation and induce a cellular response. Escherichia coli, for example, contains 32 of these systems.
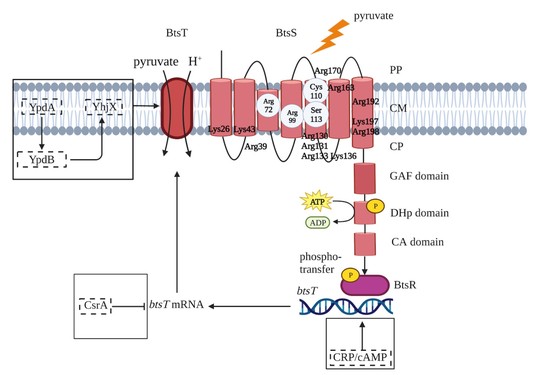
We are studying how sensing and uptake of the primary metabolite pyruvate is coordinated by the LytS/LytTR-type histidine kinase/response regulator system BtsS/BtsR and the transporter BtsT in Escherichia, Vibrio and Salmonellaspecies. Currently, our studies focus on the identification of the ligand sensed by the second LytS/LytTR-type histidine kinase/response regulator system in E. coli, the YpdA/YpdB system and the function of target gene product YhjX.
Selected Publications:
- Qiu, J., Gasperotti, A., Sisattana, N., Zacharias, M., Jung, K. (2023) The LytS-type histidine kinase BtsS is a 7-transmembrane receptor that binds pyruvate. mBio, Sep 1:e0108923. DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01089-23.
- Paulini, S., Fabiani, F.D., Weiß, A.S., Moldoveanu, A.L., Helaine, S., Stecher, B., Jung, K. (2022) The biological significance of pyruvate sensing and uptake in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Microorganisms, 10: 1751
- Göing, S., Gasperotti, A.F., Yang, Q., Defoirdt, T., Jung, K. (2021) Insights into a pyruvate sensing and uptake system in Vibrio campbellii and its importance for virulence. J. Bacteriol. 203: e00296-21
- Steiner, B.D., Eberly, A.R., Hurst, M.N., Zhang, E., Behr, S., Jung, K., Hadjifrangiskou, M. (2018) Evidence of cross-regulation in two closely-related pyruvate-sensing systems in uropathogenic Escherichia coli, J. Membr. Biol., 251(1):65-74.
- Vilhena, C., Kaganovitch, E., Shin, J.Y., Grünberger, A., Behr, S., Kristoficova, I., Brameyer, S., Kohlheyer, D., Jung, K. (2018) A single cell view of the BtsSR/YpdAB pyruvate sensing network in Escherichia coli and its biological relevance, J. Bacteriol., 200: e00536-17.
- Behr, S., Kristoficova, I., Wittig, M., Breland, E.J., Eberly, A.R., Sachs, C., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Hadjifrangiskou, M., Jung, K. (2017) Identification of a high-affinity pyruvate receptor in Escherichia coli, Sci. Rep., 7: 1388.
- Fried, L., Behr, S., Jung, K. (2013) Identification of a target gene and activating stimulus for the YpdA/YpdB histidine kinase/response regulator system in Escherichia coli, J. Bacteriol. 195: 807-815
- Kraxenberger, T., Fried, L., Behr, S., Jung, K. (2012) First insights into the unexplored two-component system YehU/YehT in Escherichia coli, J. Bacteriol. 194: 4272-4284.
Area 3
The role of RNA modifications in the stress response of bacteria and the impact on translation
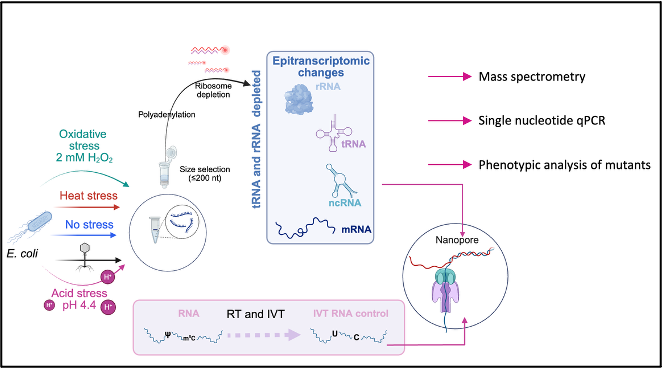
The modification of RNA is an important regulator of physiological processes in eukaryotes, but has not been thoroughly studied in prokaryotes. We have successfully established Nanopore direct RNA sequencing of bacterial RNA and investigated changes of rRNA, tRNA and mRNA modifications in Escherichia coli under heat, acid and oxidative stress as well as during phage infection. RNA sequencing is complemented by a multifaceted approach including mass spectrometry, deletion mutants, single nucleotide PCR and in vitro methylation.
Selected Publications:
- Riquelme-Barrios, S., Vasquez-Camus, L., Cusack, S.A., Burdack, K., Petrov, D.P., Yesiltac-Tosun, G. N., Kaiser, S.,Giehr, P. & Jung, K. Direct RNA sequencing of the Escherichia coli epitranscriptome uncovers alterations under heat stress. Nucleic Acids Res 53, gkaf175 (2025). https://doi.org:10.1093/nar/gkaf175
- Saikia, B., Riquelme-Barrios, S., Carell, T., Brameyer, S. & Jung, K. Depletion of m6A-RNA in Escherichia coli reduces the infectious potential of T5 bacteriophage. Microbiol Spectr 12, e0112424 (2024). https://doi.org:10.1128/spectrum.01124-24
- Petrov, D.P., Kaiser, S., Kaiser, S., Jung, K. (2022) Opportunities and challenges to profile mRNA modifications in Escherichia coli. Chembiochem. 23: e202200270 doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.202200270
- Tomasiunaite, U., Brewer, T., Burdack, K., Brameyer, S. & Jung, K. Versatile dual reporter to identify ribosome pausing motifs alleviated by translation elongation factor P. ACS Synth Biol 13, 3698-3710 (2024). https://doi.org:10.1021/acssynbio.4c00534
Area 4
How a commensal bacterium of the genus Desulfovibrio finds its niche in the gut and how this process can be stopped
The healthy human gut contains a small number of sulfate-reducing bacteria of the genus Desulfovibrio. These bacteria gain energy by respiration and transfer electrons to sulfate as an electron acceptor, which leads to the production of toxic hydrogen sulfide. For thus far unknown reasons, there is a massive proliferation of Desulfovibrio bacteria in patients suffering from inflammatory bowel disease, bacteremia, Parkinson’s disease or autism.
Despite the importance of Desulfovibrio spp. little is known how these bacteria find a niche for colonization. We hypothesize that motile Desulfovibrio spp. uses chemotaxis to swim along chemical gradients into the deep layers of the mucus. This project aims to identify the key players in the perception and chemotactic response of Desulfovibro desulfuricans.
We will develop innovative genetic engineering tools for D. desulfuricans, study the chemotactic capabilities of D. desulfuricans by a combination of motility assays and biochemical protein-ligand binding assays, and translate our findings into strategies to disturb chemotaxis, including tracking of D. desulfuricans in 2-D organoids and target-specific in situ gene editing in microbial communities.
The results of the project will not only contribute to a better understanding of the physiology of the intestinal commensals Desulfovibrio spp., which under certain conditions harm the host, but also open up a novel antimicrobial approach to restore a healthy human intestinal microbiota.
Selected Publication:
- Almeida, L., Fajardo-Ruiz, E., Brameyer, S., Jung, K. (2025) The framework for genetic engineering in Desulfovibrionaceae. ACS Synth. Biol., 14: 2445−2454 https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5c00351
Area 5
Chemical Biology and the identification of protein targets of natural compounds
There are about 500,000 molecules in the communication between pro- and eukaryotes. We use bacterial model organisms to study the effect of natural compounds such as fimbrolides, quorum quenchers or eukaryotic hormones on the phenotypic behavior of bacteria, such as quorum sensing and chemotaxis. The project also focuses on the identification of the cellular targets of these compounds.
Selected Publications:
- Mostert, D., Bubeneck, W.A., Rauh, T., Kielkowski, P., Itzen, A., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2024) Pronucleotide probes reveal a diverging specificity for AMPylation vs UMPylation of human and bacterial nucleotide transferases. Biochemistry, 63:651-659. doi: http://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00568.
- Weigert Muñoz, A., Hoyer, E., Schumacher, K., Grognot, M., Taute, K., Hacker, S., Sieber, S.A., Jung, K. (2022) Eukaryotic catecholamine hormones influence the chemotactic control of Vibrio campbellii by binding to the coupling protein CheW. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 119: e2118227119. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2118227119.
- Rauh, T., Brameyer, S., Itzen, A., Kielkowski, P., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2020) MS-based in situ proteomics reveals AMPylation of host proteins during bacterial infection, ACS Infect. Dis., 6: 3277-3289.
- Zhao, W., Lorenz, N., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2016) Mechanistic analysis of aliphatic β-lactones in Vibrio harveyi reveals a quorum sensing independent mode of action, Chem. Commun., 52: 11971-11974
- Zhao, W., Lorenz, N., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2016) Fimbrolide natural products disrupt bioluminescence of Vibrio harveyi by targeting autoinducer biosynthesis and luciferase activity, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 55(3): 1187-91.
- Rossmann, F.S., Wobser, D., Racek, T., Puchalka, J., Rabener, E.M., Reiger, M., Hendrickx, A.P.A., Diederich, A., Jung, K., Klein, C., Huebner, J. (2015) Phage-mediated dispersal of biofilm and distribution of bacterial virulence genes is induced by Quorum Sensing, PLoS Pathog., 11(2): e1004653.
- Chu, Y., Nega, M., Wölfle, M., Plener, L., Grond, S., Jung, K., Götz, F. (2013) A new class of quorum quenching molecules from Staphylococcus species affects communication of Gram-negative bacteria, PLoS Pathog., 9(9): e1003654.
2025
Almeida, L., Fajardo-Ruiz, E., Brameyer, S., Jung, K. (2025) The framework for genetic engineering in Desulfovibrionaceae. ACS Synth. Biol., https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5c00351.
Vasquez-Camus, L., Riquelme-Barrios, S., Jung, K. (2025) Detection of stress-dependent m5C rRNA dynamics in Escherichia coli using m5C-Rol-LAMP, bioRxiv 2025.06.13.659538; https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.13.659538.
Riquelme Barrios, S., Vasquez Camus, L., Cusack, S.A., Burdack, K., Petrov, D.P., Yeşiltaç-Tosun, N., Kaiser, S., Giehr, P.*, Jung, K.* (2025) Direct RNA sequencing of the Escherichia coli epitranscriptome uncovers alterations under heat stress, Nucleic Acid Res.,53; gkaf175. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf175.
2024
Saikia, B., Riquelme Barrios, S., Carell, T., Brameyer, S.*, Jung, K.* (2024) Depletion of m6A-RNA in Escherichia coli reduces the infectious potential T5 bacteriophage, Microbiol. Spectr., 18:e0112424. doi:10.1128/spectrum.01124-24. Online ahead of print.
Han, Z., Panhans, S., Brameyer, S., Bilgen, E., Ram,M. , Herr, A., Narducci, A., Isselstein, M., Harris, P-D., Brix, O., Jung, K., Lamb, D.C., Lerner, E., Griffith, D., Weikl, T.R, Zijlstra, N., Cordes, T. (2024) Dissecting mechanisms of ligand binding and conformational changes in the glutamine binding protein. eLife, 13:RP95304.
Tomasiunaite, U., Brewer, T., Burdack, K., Brameyer, S., Jung, K. (2024) A versatile dual reporter to identify ribosome pausing motifs alleviated by translation elongation factor P. ACS Synth. Biol., https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.4c00534.
Riquelme Barrios, S., Vasquez Camus, L., Cusack, S.A., Burdack, K., Petrov, D.P., Yeşiltaç-Tosun, N., Kaiser, S., Giehr, P., Jung, K. (2024) Direct RNA sequencing of the Escherichia coli epitranscriptome uncovers alterations under heat stress, Nucleic Acid Res., submitted, bioRxiv 2024.07.08.602490. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.08.602490.
Mostert, D., Bubeneck, W.A., Rauh, T., Kielkowski, P., Itzen, A., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2024) Pronucleotide probes reveal a diverging specificity for AMPylation vs UMPylation of human and bacterial nucleotide transferases. Biochemistry, 63:651-659. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00568.
Tomasiunaite, U., Kielkowski, P., Krafczyk, R., Forné, I., Imhof, A., Jung, K. (2024) Decrypting the functional design of unmodified translation elongation factor P. Cell Rep., 43:114063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114063.
Schumacher, K., Braun, D., Kleigrewe, K., Jung, K. (2024) Motility-activating mutations upstream of flhDC reduce acid shock survival of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr.,12:e0054424. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.00544-24.
Ramos Ricciuti, F.E., Herrera Seitz, M.K., Gasperotti, A.F., Boyko, A., Jung, K., Bellinzoni, M., Lisa, M.-N., Studdert, C.A. (2024) The chemoreceptor controlling the Wsp-like transduction pathway in Halomonas titanicae KHS3 binds and responds to purine derivatives. FEBS J., https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.17320.
2023
Vinacour, M., Moiana, M., Forné, I., Jung, K., Valdayo, P.M.C., Nikel, P.I., Imhof, A., Palumbo, M.C., Do Porto, D.F., Ruiz, J.A. (2023) Genetic dissection of the degradation pathways for the mycotoxin fusaric acid in Burkholderia ambifaria T16. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 89:e0063023. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00630-23.
Schumacher, K., Gelhausen, R., Backofen, R., Kion-Crosby, W., Barquist, L., Jung, K. (2023) Ribosome profiling reveals the fine-tuned response of Escherichia coli to acid stress. mSystems, Nov 1:e0103723; https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/msystems.01037-23.
Qiu. J., Gasperotti, A., Sisattana, N., Zacharias, M., Jung, K. (2023) The LytS-type histidine kinase BtsS is a 7-transmembrane receptor that binds pyruvate. mBio, Sep 1:e0108923. DOI: 10.1128/mbio.01089-23.
Schumacher, K., Brameyer, S., Jung, K. (2023) Bacterial acid stress response: from cellular changes to antibiotic tolerance and phenotypic heterogeneity. Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 75: 102367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2023.102367.
Schwarz, J., Brameyer, S., Hoyer, E., Jung, K. (2023) The interplay of AphB and CadC to activate acid resistance of Vibrio campbellii. J. Bacteriol, 205:e0045722. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00457-22.
2022
Schwarz, J., Schumacher, K., Brameyer, S.*, Jung, K.* (2022) Battle of bacteria against acidity, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuac037
Gabold, B., Adams, F., Brameyer, S., Jung, K., Ried, C.L., Merdan, T., Merkel, O.M. (2022) Transferrin-modified chitosan nanoparticles for targeted nose-to-brain delivery of proteins. Drug Delivery and Translational Research, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-022-01245-z.
Paulini, S., Fabiani, F.D., Weiß, A.S., Moldoveanu, A.L., Helaine, S., Stecher, B., Jung, K. (2022) The biological significance of pyruvate sensing and uptake in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Microorganisms, 10: 1751.
Petrov, D.P., Kaiser, S., Kaiser, S.*, Jung, K*. (2022) Opportunities and challenges to profile mRNA modifications in Escherichia coli. Chembiochem., 23: e202200270.
Brameyer, S., Schumacher, K., Kuppermann, S., Jung, K. (2022) Division of labor and collective functionality in Escherichia coli under acid stress. Commun. Biol., 5: 327.
Weigert Muñoz, A., Hoyer, E., Schumacher, K., Grognot, M., Taute, K., Hacker, S., Sieber, S.A.*, Jung, K.* (2022) Eukaryotic catecholamine hormones influence the chemotactic control of Vibrio campbellii by binding to the coupling protein CheW. PNAS, 119 (10): e211822711.
Weiss, A.S., Burrichter, A.G., Durai Raj, A.C., von Strempel, A., Meng, C., Kleigrewe, K., Münch, P.C., Rössler, L., Huber, C., Eisenreich, W., Jochum, L.M., Göing, S., Jung, K., Lincetto, C., Hübner, J., Marinos, G., Zimmermann, J., Kaleta, C., Sanchez, A., Stecher, B. (2022) In vitro interaction network of a synthetic gut bacterial community. ISME J., 16(4):1095-1109.
2021
Göing, S., Gasperotti, A.F., Yang, Q., Defoirdt, T., Jung, K. (2021) Insights into a pyruvate sensing and uptake system in Vibrio campbellii and its importance for virulence. J Bacteriol., 203:e00296-21
Göing, S., Jung, K. (2021) Viable but nonculturable gastrointestinal bacteria and their resuscitation. Arch. Gastroenterol. Res., 2: 55-62.
Krafczyk, R., Qi, F., Sieber, A., Mehler, J., Jung, K., Frishman, D., Lassak, J. (2021) Proline codon pair selection determines ribosome pausing strength and translation efficiency in bacteria, Commun. Biol., 4: 589.
Gasperotti, A.F., Herrera Seitz, M.K., Balmaceda, R.S., Prosa, L.M., Jung, K.*, Studdert, C.A.* (2021) Direct binding of benzoate derivatives to two chemoreceptors with Cache sensor domains in Halomonas titanicae KHS3. Mol. Microbiol., 115: 672-683.
Martini, L., Brameyer, S., Hoyer, E., Jung, K.*, Gerland, U.* (2021) Dynamics of chromosomal target search by a membrane-integrated one-component receptor. PLoS Comp Biol., 17: e1008680.
Pinheiro, B., Petrov, D.P., Guo, L., Martins, G.B., Bramkamp, M., Jung, K. (2021) Elongation factor P is required for EIIGlc translation in Corynebacterium glutamicum due to an essential polyproline motif. Mol. Microbiol., 115 (2): 320-331. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14618. Epub 2020 Oct 25. PMID: 3301208.
Pfab, M., Kielkowski, P., Krafczyk, R., Volkwein, W., Sieber, S.A., Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2021) Synthetic post-translational modifications of elongation factor P using the ligase EpmA. FEBS J., 288: 663-677.
2020
Gasperotti, A.F., Göing, S., Fajardo-Ruiz, E., Forne, I., Jung, K. (2020) Function and regulation of the pyruvate ransporter CstA in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 21, E9068.
Rauh, T., Brameyer, S., Itzen, A., Kielkowski, P., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2020) MS-based in situ proteomics revealy AMPylation of host proteins during bacterial infection. ACS Infect. Dis., 6: 3277-3289.
Brameyer, S., Hoyer, E., Bibinger, S., Burdack, K., Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2020) Molecular design of a signaling system influences noise in protein abundance under acid stress in different gamma-proteobacteria. J Bacteriol., 202: e00121-20.
Pinheiro, B., Scheidler, C.M., Kielkowski, P., Schmid, M., Forné, I., Ye, S., Reiling, N., Takano, E., Imhof, A., Sieber, S. A., Schneider, S., Jung, K. (2020) Structure and function of a novel elongation factor P subfamily in Actinobacteria. Cell Rep., 30: 4332-4342.e5.
Gasperotti, A., Brameyer, S., Fabiani, F., Jung, K. (2020) Phenotypic heterogeneity of microbial populations under nutrient limitation. Curr. Opin. Biotechn., 62: 160–167.
2019
Jung, K., Brameyer, S., Fabiani, F., Gasperotti, A., Hoyer, E. (2019) Phenotypic heterogeneity generated by histidine kinase-based signaling networks. J. Mol. Biol., 431: 4547-4558.
Reichle, V. F., Petrov, D. P., Weber, V., Jung, K. & Kellner, S. (2019) NAIL-MS reveals the repair of 2-methylthiocytidine by AlkB in E. coli. Nat. Commun., 10: 5600.
Volkwein, W., Krafczyk, R., Kumar, P.A.J., Parr, M., Mankina, E., Macošek, J., Guo, Z., Fürst, M.J.L.J., Pfab, M., Frishman, D., Hennig, J., Jung, K., Lassak, J. (2019) Switching the post-translational modification of translation elongation factor EF-P. Front. Microbiol., 10: 1148.
Kandil, R., Xie, Y., Heermann, R., Isert, L., Jung, K., Mehta, A., Merkel, O.M. (2019) T Cell Transfection: Coming in and finding out: blending receptor‐targeted delivery and efficient endosomal escape in a novel bio‐responsive siRNA delivery system for gene knockdown in pulmonary T-cells. Adv. Therap., 2: 1970015.
This work was awarded with the PHOENIX Wissenschaftspreis 2020
Vilhena, C., Kaganovitch, E., Grünberger, A., Motz, M., Forné, I., Kohlheyer, D., Jung, K. (2019) Importance of pyruvate sensing and transport for the resuscitation of viable but nonculturable Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol., 201: e00610-18.
Brameyer, S., Rösch, T.C., Andarib, J.A., Hoyer, E., Schwarz, J., Graumann, P.L., Jung, K. (2019) DNA-binding directs the localization of a membrane-integrated receptor of the ToxR family. Commun. Biol., 2: 4.
Nickel, C., Horneff, R., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Soll, J., Schwenkert, S. (2019) Phosphorylation of the outer membrane mitochondrial protein OM64 influences protein import into mitochondria. Mitochondrion, 44: 93-102.
2018
Stockmar, I., Feddersen, H., Cramer, K., Gruber, S., Jung, K., Bramkamp, M., Shin, J. Y. (2018) Optimization of sample preparation and green color imaging using the mNeonGreen fluorescent protein in bacterial cells for photoactivated localization microscopy. Sci. Rep., 8(1): 10137.
Brameyer, S., Plener, L., Müller, A., Klingl, A., Wanner, G., Jung, K. (2018) Outer membrane vesicles facilitate trafficking of the hydrophobic signalling molecule CAI-1 between Vibrio harveyi cells. J. Bacteriol., 200(15): e00740-17.
Selected as Spotlight: Outer membrane vesicles as vehicle for hydrophobic quorum sensing molecules
Motz, L., Jung, K. (2018) The role of polyproline motifs in the histidine kinase EnvZ. PLoS One, 13(6): e0199782.
Jung, K., Fabiani, F., Hoyer, E., Lassak, J. (2018) Bacterial transmembrane signalling systems and their engineering for biosensing. Open Biol., 8: 180023.
Steiner, B.D., Eberly, A.R., Hurst, M.N., Zhang, E., Behr, S., Jung, K., Hadjifrangiskou, M. (2018) Evidence of cross-regulation in two closely-related pyruvate-sensing systems in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Membr. Biol., 251(1): 65-74.
Qi, F., Motz, M., Jung, K., Lassak, J. and Frishman, D. (2018) Evolutionary analysis of polyproline motifs in Escherichia coli reveals their regulatory role in translation. PLoS Comput. Biol., 14(2): e1005987.
Stecher, B., Jung, K. (2018) LACTATEing Salmonella: a host-derived fermentation product fuels pathogen growth. Cell Host Microbe, 23(1): 3-4.
Vilhena,C., Kaganovitch, E., Shin, J.Y., Grünberger, A., Behr, S., Kristoficova, I., Brameyer, S., Kohlheyer, D., Jung, K. (2018) A single cell view of the BtsSR/YpdAB pyruvate sensing network in Escherichia coli and its biological relevance. J. Bacteriol., 200: e00536-17.
Kristoficova, I., Vilhena, C., Behr, S., Jung, K. (2018) BtsT - a novel and specific pyruvate/H+ symporter in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 200: e00599-17.
Selected as spotlight: Identification of the First Pyruvate Transporter in Escherichia coli
2017
Krafczyk, R., Macošek, J., Jagtap, P.K.A., Gast, D., Wunder, S., Mitra, P., Jha, A.K., Rohr, J., Hoffmann-Röder, A., Jung K, Hennig, J., Lassak, J. (2017) Structural basis for EarP-mediated arginine glycosylation of translation elongation factor EF-P. mBio., 8: e01412-17.
Parvin, N., Carrie, C., Pabst, I., Läßer, A., Paul, M., Geigenberger, P., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Vothknecht, U.C., Chigri, F. (2017) TOM9.2: a calmodulin-binding protein essential for TOM complex assembly in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant., 10: 575-589.
Mörk-Mörkenstein, M., Heermann, R., Göpel, Y., Jung, K., Görke, B. (2017) Non-canonical activation of histidine kinase KdpD by phosphotransferase protein PtsN through interaction with the transmitter domain. Mol. Microbiol., 106: 54-73.
Behr, S., Brameyer, S., Witting, W., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Jung, K. (2017) Comparative genomics of LytS/LytTR histidine kinase/response regulator systems in γ-proteobacteria. PloS One, 12(8): e0182993.
Volkwein, W., Maier, C., Krafczyk, R., Jung, K.*, Lassak, J.* (2017) A versatile toolbox for the control of protein levels using Nε-acetyl-L-lysine dependent amber suppression. ACS Synth. Biol., 6: 1892-1902.
Behr, S., Kristoficova, I., Wittig, M., Breland, E.J., Eberly, A.R., Sachs, C., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Hadjifrangiskou, M., Jung, K. (2017) Identification of a high-affinity pyruvate receptor in Escherichia coli. Sci. Rep., 7: 1388.
Schlundt, A., Buchner, S., Janowski, R., Heydenreich, T., Heerman, R., Geerlof, A., Stehle, R., Niessing, D., Jung, K., Sattler, M. (2017) Structure and activity of the DNA-binding domain of a transmembrane transcriptional activator. Sci. Rep., 7: 1051.
Wang, Y., Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2017) CipA and CipB as scaffolds to organize proteins into crystalline inclusions. ACS Synth. Biol., 6: 826-836.
Fang, C., Staroń, A., Grafe, M., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Gebhard, S., Mascher, T. (2017) Insulation and wiring specificity determinants of BceR-like response regulators and their target promoters in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol., 104: 16-31.
Schramke, H., Laermann, V., Tegetmeyer, H.E., Brachmann, A., Jung, K.*, Altendorf, K*. (2017) Revisiting regulation of potassium homeostasis in Escherichia coli: the connection to phosphate limitation. MicrobiologyOpen, 6, e00438.
Lorenz, N., Shin, J.Y., Jung, K. (2017) Activity, abundance and localization of quorum sensing receptors in Vibrio harveyi. Front. Microbiol., 8: 634.
2016
Li, X., Krafczyk, R., Macoşek, J., Li, Y.-L., Zou, Y., Simon, B., Pan, X., Wu, Q.-Y., Yan, F, Li, S., Hennig, J., Jung, K., Lassak, J., Hu, H.-G. (2016) Resolving the α-glycosidic linkage of arginine-rhamnosylated translation elongation factor P (EF-P) triggers generation of the first ArgRha specific antibody. Chem. Sci., 7: 6995-7001.
Lemfack, M.C., Ravella, S.R., Lorenz, N., Kai, M., Jung, K., Schulz, S., Piechulla, B. (2016) Novel volatiles of the skin-borne bacteria inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and affect Quorum-Sensing controlled phenotypes of Gram-negative bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol., 39: 503-515.
Jung, K. (2016) Die Kommunikation von Bakterien. pp. 117-126. In: Bayer. Akademie der Wissenschaften (Hrsg.): Die Sprache der Moleküle – Chemische Kommunikation in der Natur. Pfeil., München.
Zhao, W., Lorenz, N., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2016) Mechanistic analysis of aliphatic β-lactones in Vibrio harveyi reveals a quorum sensing independent mode of action. Chem. Commun., 52, 11971-11974.
Schramke, H., Tostevin, F., Heermann, R., Gerland, U., Jung, K. (2016) A dual-sensing receptor confers robust cellular homeostasis. Cell Rep., 16: 213–221.
Lorenz, N., Reiger, M., Toro-Nahuelpan, M., Brachmann, A., Poettinger, L., Plener, L., Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2016) Identification and initial characterization of prophages in Vibrio campbellii. PLoS One, 11: e0156010.
Behr, S., Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2016) Insights into the DNA-binding mechanism of a LytTR-type transcription regulator. Biosci. Rep., 36: e00326.
Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2016) Don’t stop me now! labor&more, 2.
Hörnschemeyer, P., Liss, V., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Hunke, S. (2016) Interaction analysis of a two-component system using nanodiscs. PLoS One, 11(2): e0149187.
Zhao, W., Lorenz, N., Jung, K., Sieber, S.A. (2016) Fimbrolide natural products disrupt bioluminescence of Vibrio harveyi by targeting autoinducer biosynthesis and luciferase activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 55 (3):1187-91.
Lassak, J., Wilson, D.N., Jung, K. (2016) Stall no more at polyproline stretches with the translation elongation factors EF-P and IF-5A. Mol. Microbiol., 99 (2): 219–235.
2015
Moscoso, J.A., Schramke, H., Zhang, Y., Tosi, T., Dehbi, A., Jung, K., Gründling, A. (2015) Binding of c-di-AMP to the Staphylococcus aureus sensor kinase KdpD occurs via the USP domain and down-regulates the expression of the Kdp potassium transporter. J. Bacteriol., 198 (1): 98-110.
Buchner, S., Schlundt, A., Lassak, J., Sattler, J., Jung, K. (2015) The role of a disordered linker in the pH-sensor CadC of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol., 427(15): 2548-2561.
Rossmann, F.S., Wobser, D., Racek, T., Puchalka, J., Rabener, E.M., Reiger, M., Hendrickx, A.P.A., Diederich, A., Jung, K., Klein, C., Huebner, J. (2015) Phage-mediated dispersal of biofilm and distribution of bacterial virulence genes is induced by Quorum Sensing. PLoS Pathog., 11(2): e1004653.
Ruiz, J.A., Bernar, E.M., Jung, K. (2015) Production of siderophores increases resistance to fusaric acid in Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5. PLoS One, 10(1): e0117040.
Reiger, M., Lassak, J., Jung, K. (2015) Deciphering the role of the type II glyoxalase isoenzyme YcbL (GlxII-2) in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 362: 1-7.
Lassak, J., Keilhauer, E., Fürst, M., Wuichet, K., Gödeke, J., Starosta, A.L., Chen, J., Søgaard-Andersen, L., Rohr, J., Wilson, D.N., Häussler, S., Mann, M., Jung, K. (2015) Arginine-rhamnosylation as new strategy for post-translational modification of translation elongation factor P. Nat. Chem. Biol., 11: 266-70.
- Comment: Tonetti, M. G. (2015) Translation from sticky to sweet. Nat. Chem. Biol., 11: 243-244.
Plener, L., Lorenz, N., Reiger, M., Ramalho, T., Gerland, U., Jung, K. (2015) The phosphorylation flow of the Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing cascade determines levels of phenotypic heterogeneity in the population. J. Bacteriol., 197: 1747–1756.
Selected as spotlight: Phenotypic heterogeneity generated by the Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing cascade
Schramke, H., Wang, Y., Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2015) Stimulus perception by histidine kinases. In de Bruijn, F.J. (Editor) Stress and environmental control of gene expression in bacteria. Wiley-Blackwell Publishers.
2014
Rauschmeier, M., Schüppel, V., Tetsch, L., Jung, K. (2014) New insights into the interplay between the lysine transporter LysP and the pH sensor CadC in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol., 426: 1215–1229.
Fritz, G., Megerle, J.A., Westermayer, S.A., Brick, D., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Rädler, J.O., Gerland, U. (2014) Single cell kinetics of phenotypic switching in the arabinose utilization system of E. coli. PLoS One, 9(2): e89532.
Heermann, R., Zigann, K., Gayer, S., Rodriguez-Fernandez, M., Banga, J.R., Kremling, A., Jung, K. (2014) Dynamics of an interactive network composed of a bacterial two-component system, a transporter and K+ as mediator. PLoS One, 9(2): e89671.
Drees, B., Reiger, M., Jung, K., Bischofs, I.B. (2014) A biophysical taxonomy of encoder network modules in bacterial quorum sensing systems. Biophys. J., 107: 266–277.
Behr, S., Fried, L., Jung, K. (2014) Identification of a novel nutrient-sensing histidine kinase/response regulator signaling network in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 96: 2023-2029.
Dintner, S., Heermann, R., Fang, C., Jung, K., Gebhard, S. (2014) A sensory complex consisting of an ATP-binding-cassette transporter and a two-component regulatory system controls bacitracin resistance in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem., 289: 27899-27910.
Starosta, A.L., Lassak, J., Atkinson, G.C., Peil, L., Woolstenhulme, C.J., Virumäe, K., Buskirk, A., Tenson, T., Remme, J., Jung, K., Wilson, D.N. (2014) A conserved proline triplet in Val-tRNA synthetase and the origin of elongation factor P. Cell Rep., 9: 476-483.
Starosta, A.L., Lassak, J., Peil, L., Atkinson, G.C., Virumäe, K., Tenson, T., Remme, J., Jung, K., Wilson, D.N. (2014) Translational stalling at polyproline-stretches is modulated by the context of the stall site. Nucleic Acid Res., 42: 10711-10719.
Lassak, J., Fried, L., Jung, K. (2014) Angestaubt aber nicht eingerostet - Der Bioreporter LacZ. Biospektrum 20, 510-513
Josenhans, C., Jung, K., Rao, C.V., Wolfe, A.J. (2014) A tale of two machines: A review of the BLAST meeting, Tucson, AZ, January 20-24, Mol. Microbiol., 91: 6-25.
Starosta, A.L., Lassak, J., Jung, K., Wilson, D.N. (2014) The bacterial translation stress response. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 38: 1172-11201.
2013
Hornung, C., Poehlein, A., Haack, F.S., Schmidt, M., Dierking, K., Pohlen, A., Schulenburg, H., Blokesch, M., Plener, L., Jung, K., Bonge, A., Utpatel, C., Timmermann, G., Pommerening-Röser, A., Bode, E., Bode, H.B., Daniel, R., Schmeisser, C., Streit, W.R. (2013) Genome analysis of Janthinobacterium sp. HH01 reveals the presence of a single autoinducer synthase gene (jqsA) involved in the synthesis of a novel CAI-1-like signaling molecule. PLoS One, 8(2): e55045.
Ude, S., Lassak, J., Starosta, A. L., Kraxenberger, T., Wilson, D.N., Jung, K. (2013) Translation elongation factor EF-P alleviates ribosome stalling at polyproline stretches. Science, 339: 82-85.
- Comment in Biochemistry. Getting past polyproline pauses. [Science. 2013]
- „Smooth translation“ Lab Times 3, 2013
- „Keine Pause bei Prolinen: Elongationsfaktor EF-P rettet die Proteinsynthese“ BIOspektrum 03, 2013
- „Kontrollstopp für die Eiweißsynthese“ LMU Einsichten, 2013
- „Translation von Polyprolin-Proteinen“ J. Lassak, S. Ude, A. L. Starosta, D. N. Wilson, K. Jung (2013) BIOspektrum 19: 616-618.
Fried, L., Behr, S., Jung, K. (2013) Identification of a target gene and activating stimulus for the YpdA/YpdB histidine kinase/response regulator system in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 195: 807-815.
Chu, Y., Nega, M., Wölfle, M., Plener, L., Grond, S., Jung, K., Götz, F. (2013) A new class of quorum quenching molecules from Staphylococcus species affects communication of Gram-negative bacteria. PLoS Pathog., 9(9): e1003654.
Peil, L., Starosta, A.L., Lassak, J., Atkinson, G., Virumäe, K., Spitzer, M., Tenson, T., Jung, K., Remme, J., Wilson, D.N. (2013) Distinct XPPX-motifs induce ribosome stalling, which are rescued by the translation elongation factor EF-P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110: 15265-15270.
- Comment in VBIO: Molekularbiologie: Schlüsselfaktor mit breiter Wirkung
Schweiger, R., Soll, J., Jung, K., Heermann, R., Schwenkert, S. (2013) Quantification of interaction strengths between chaperones and tetratricopeptide repeat domain containing membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem., 288: 30614-30625.
Lassak, J., Ude, S. Starosta, A.L., Wilson, D.N., Jung, K. (2013) Translation von Polyprolin-Proteinen. Biospektrum, 19: 616-618.
2012
Kraxenberger, T., Fried, L., Behr, S., Jung, K. (2012) First insights into the unexplored two-component system YehU/YehT in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 194: 4272-4284.
Haneburger, I., Fritz, G., Jurkschat, N., Tetsch, L., Eichinger, A., Skerra, A., Gerland, U., Jung, K. (2012) Deactivation of the E. coli pH stress sensor CadC by cadaverine. J. Mol. Biol., 424: 15-27.
Anetzberger, C., Reiger, M., Fekete, A., Schell, U., Stambrau, N., Plener, L., Kopka, J., Schmitt-Kopplin, P., Hilbi, H., Jung, K. (2012) Autoinducers act as biological timers in Vibrio harveyi. PLoS One, 7(10): e48310.
Anetzberger, C., Schell, U., Jung, K. (2012) Single cell analysis of Vibrio harveyiuncovers functional heterogeneity in response to quorum sensing signals. BMC Microbiol., 12: 209.
Fried L., Lassak J., Jung K. (2012) A comprehensive toolbox for the rapid construction of lacZ fusion reporters. J. Microbiol. Meth., 91(3): 537-543.
Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2012) K+ supply, osmotic stress, and the KdpD/KdpE two-component system. pp. 181-199. In Gross, R., Baier, D. (eds.) Two-component systems. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk
2011
Eichinger, A., Haneburger, I., Koller, C., Jung, K., Skerra, A. (2011) Crystal structure of the sensory domain of Escherichia coli CadC, a member of the ToxR-like protein family. Protein Sci., 20: 656-669.
Haneburger, I., Eichinger, A., Skerra, A., Jung, K. (2011) New insights into the signaling mechanism of the pH-responsive membrane-integrated transcriptional activator CadC of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 286: 10681-10689.
Ruiz, J., Haneburger, I., Jung, K. (2011) ArgP and Lrp differentially regulate transcription of lysP, the gene encoding the specific lysine permease of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 193: 2536-2548.
Tetsch, L., Koller, C. Dönhöfer, A., Jung, K. (2011) Detection and function of an intramolecular disulfide bond in the pH-responsive CadC of Escherichia coli. BMC Microbiol., 11: 74.
Jung, K., Fried, L., Behr, S., and Heermann, R. (2011) Histidine Kinases and Response Regulators in Networks. Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 15: 1–7.
Jung, K. (2011) Tuning communication fidelity. Nature Chem. Biol., 7: 502-503.
2010
Heermann, R., Jung K (2010) The complexity of the „simple“ two-component-system KdpD/KdpE in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microb. Lett., 304: 97-106.
2009
Heermann, R., Weber, A., Mayer, B., Ott, M., Hauser, E., Gabriel, G., Pirch, T., Jung, K. (2009) The universal stress protein UspC scaffolds the KdpD/KdpE signaling cascade of Escherichia coli under salt stress. J. Mol. Biol., 386: 134-148.
Lüttmann, D., Heermann, R., Zimmer, B., Hillmann, A., Rampp I.S., Jung, K., Görke, B. (2009) Stimulation of the potassium sensor KdpD kinase activity by interaction with the phosphotransferase protein IIANtr in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol., 72: 978-994.
Anetzberger, C., Pirch, T., Jung, K. (2009) Heterogeneity in quorum sensing regulated bioluminescence of Vibrio harveyi. Mol. Microbiol., 73: 267–277.
Heermann, R., Lippert, M.-L., Jung, K. (2009) Domain swapping reveals that the N-terminal domain of the sensor kinase KdpD in Escherichia coli is important for signaling. BMC Microbiology, 9: 133.
Fritz, G., Koller, C., Tetsch, L., Haneburger, I., Burdack, K., Jung, K., Gerland, U. (2009) Induction kinetics and feedback inhibition of a conditional stress response system in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol., 393: 272–286.
Tetsch, L., Jung, K. (2009) The regulatory interplay between membrane-integrated sensors and transporters in bacteria. Mol. Microbiol., 73: 982-991.
Jung, K., Jung, H. (2009) A new mechanism of phospho-regulation in signal transduction pathways. Sci. Signal., 2: pe71.
Jiménez-Soto, L.F., Kutter, S., Sewald, X., Ertl, C., Weiss, E., Kapp, U., Rohde, M., Pirch, T., Jung, K., Retta, SF, Terradot, L., Fischer, W., Haas, R. (2009) Helicobacter pylori type IV secretion apparatus exploits β1 integrin in a novel RGD-independent manner. PLoS Pathog., 5(12): e1000684.
Tetsch, L., Jung, K. (2009) How are signals transduced across the cytoplasmic membrane? Transport proteins as transmitter of information. Amino Acids, 37: 467-477.
Krämer, R., Jung, K. (2009) (Editors) Bacterial Signaling. Wiley-VCH Verlag Weinheim
Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2009) Stimulus Perception and Signaling in Histidine Kinases. In Krämer, R., Jung, K. (eds.) Bacterial Signaling. Wiley-VCH Verlag Weinheim
Anetzberger, C. Jung, K. (2009) Intercellular communication. In Krämer, R., Jung, K. (eds.) Bacterial Signaling. Wiley-VCH Verlag Weinheim
2008
Tetsch, L., Koller, C., Haneburger, I., Jung, K. (2008) The membrane-integrated transcriptional activator CadC of Escherichia coli senses lysine indirectly via the interaction with the lysine permease LysP. Mol. Microbiol., 67: 570-583.
Megerle, J., Fritz, G., Gerland, U., Jung, K., Rädler, J. (2008) Timing and dynamics of single cell gene expression in the arabinose utilization system. Biophys. J., 95: 2103-2115.
Heermann, R., Zeppenfeld, T. und Jung, K. (2008) Simple generation of site directed point mutations in the Escherichia coli chromosome using Red/ET recombination. Microb. Cell Fact., 7: 14-22.
Münch, A., Stingl, L., Jung, K., Heermann, R. (2008) Photorhabdus luminescens genes induced upon insect infection. BMC Genomics, 9: 229-246.
Raba, M., Baumgartner, T., Klempahn, K., Härtel, T., Hilger, D, Jung, K., Jung, H. (2008) Function of transmembrane domain IX in the Na+/proline transporter PutP. J. Mol. Biol., 382: 884-893.
2007
Jung, K., Timmen, M., Odenbach, T. (2007) Membrane topology of the quorum sensing hybrid histidine kinase LuxN of Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol., 189: 2945-2948.
Gonzalez; O.R., Küper, C., Jung, K., Naval, P.C., Mendoza, E. (2007) Parameter estimation using simulated annealing for S-system models of biochemical networks. Bioinformatics, 23: 480-486.
Fleischer, R., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Hunke, S. (2007) Purification, reconstitution and characterization of the CpxRAP envelope stress system of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 282: 8583-8593.
Zimmann, P., Steinbrügge, A., Schniederberend, M., Jung, K., Altendorf, K. (2007) The extension of the fourth transmembrane helix of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli is involved in sensing. J. Bacteriol., 189: 7326-7334.
2006
Weber, A., Jung, K. (2006) Biochemical properties of UspG, a universal stress protein of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry, 45: 1620-1628.
Timmen, M., Bassler, B. L., Jung, K. (2006) AI-1 influences the kinase activity but not the phosphatase activity of LuxN of Vibrio harveyi. J. Biol. Chem., 281: 24398-24404.
Weber, A., Kögl, S., Jung, K. (2006) Time-dependent proteome alterations under osmotic stress during aerobic and anaerobic growth conditions in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol., 188: 7165-7175.
2005
Küper, C., Jung, K. (2005) CadC mediated activation of the cadBA promoter in Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 10: 26-39.
2004
Kremling, A., Heermann, R., Centler, F., Jung, K., Gilles, E.D. (2004) Analysis of two-component signal transduction by mathematical modeling using the KdpD/KdpE system of Escherichia coli. BioSystems, 78: 23-37.
Heermann, R., Jung, K. (2004) Structural Features and Mechanisms for Sensing High Osmolarity in Microorganisms. Curr. Op. Microbiol., 7: 168-174.
2003
Heermann, R., Fohrman, A., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (2003) The transmembrane domains of the sensor kinase KdpD of E. coli are not essential for sensing K+ limitation. Mol. Microbiol., 47: 839-848.
Heermann, R., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (2003) The N-terminal input-domain of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli stabilizes the interaction between the cognate response regulator KdpE and the corresponding DNA-binding site. J. Biol. Chem., 278: 51277-51284.
Jung, K. and Altendorf, K. (2003) Stimulus perception and signal transduction by the KdpD/KdpE system of Escherichia coli. in “Regulatory Networks in Prokaryotes” (eds. P. Dürre, B. Friedrich) pp. 53-58, Norfolk, Horizon Scientific Press.
Jung, K. und Heermann, R. (2003) Die Komplexität bakterieller Histidinkinase/ Antwort-regulator-Systeme. Biospektrum 9, 456-459.
2002
Ballal, A., Heermann, R., Jung, K., Gassel, M., Apte, S.K., Altendorf, K. (2002) A chimeric Anabaena/Escherichia coli KdpD protein (Anacoli KdpD) functionally interacts with E. coli KdpE and activates kdp expression in E. coli. Arch. Microbiol., 178: 141-148.
Weber, A., Jung, K. (2002) Profiling early osmostress-dependent gene expression in Escherichia coli using DNA macroarrays. J. Bacteriol., 184: 5502-5507.
Jung, H., Buchholz, M., Clausen, J., Nietschke, M., Revermann, A., Schmid, R., Jung, K. (2002) CaiT of Escherichia coli: a new transporter catalyzing L-carnitine/γ-butyrobetaine exchange. J. Biol. Chem., 277: 39251-39258.
Stallkamp, I., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (2002) Amino acid replacements in transmembrane domain 1 influence osmosensing but not K+ sensing by the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol., 178: 525-530.
Jung, K. and Altendorf, K. (2002) Towards an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of stimulus perception and signal transduction by the KdpD/KdpE system of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 4: 223-228.
2001
Jung, K., Krabusch, M., Altendorf, K. (2001) Cs+ induces the kdp operon by lowering the intracellular K+ concentration. J. Bacteriol., 183: 3800-3803.
Jung, K., Hamann, K., Revermann, A. (2001) K+ stimulates specifically the autokinase activity of purified and reconstituted EnvZ of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 276: 40896-40902.
2000
Perraud, A.-L., Rippe, K., Bantscheff, M., Glockner, M., Lucassen, M., Jung, K., Sebald, W., Weiss, V., Gross, R. (2000) Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the response regulators and isolated signalling domains of the EvgAS and BvgAS phosphorelay systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1478: 341-354.
Heermann, R., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (2000) The hydrophilic N-terminal domain complements the membrane-anchored C-terminal domain of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 17080-17085.
Jung, K., Veen, M., Altendorf, K. (2000) K+ and ionic strength directly influence the autophosphorylation activity of the putative turgor sensor of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 40142-40147.
Brandon, L., Dorus, S., Epstein, W., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (2000) Modulation of KdpD phosphatase implicated in the physiological expression of the Kdp ATPase of Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol., 38: 1086-1092.
Jung, K. (2000) Wahrnehmung von Umweltreizen bei Bakterien. Biospektrum 6, 281-282.2001.
1999
Stallkamp, I., Dowhan, W., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (1999) Negatively charged phosphoplipids influence the activity of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli. Arch. Microbiol., 172: 295-302.
1998
Bouché, S., Klauck, E., Fischer, D., Lucassen, M., Jung, K., Hengge Aronis, R. (1998) Regulation of RssB-dependent proteolysis in Escherichia coli: A role for acetyl phosphate in a response regulator controlled process. Mol. Microbiol., 27: 787-795.
Jung, K., Heermann, R., Meyer, M., Altendorf, K. (1998) Effect of cysteine replacements on the properties of the turgor sensor KdpD of Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1372: 311-322.
Jung, K., Altendorf, K. (1998) Truncation of amino acids 12 to 128 causes deregulation of the phosphatase activity of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 273: 17406-17410.
Jung, H., Tebbe, S., Schmid, R., Jung, K. (1998) Unidirectional reconstitution and characterization of purified Na+/proline transporter of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry, 37: 11083-11088.
Jung, K., Altendorf, K. (1998) Individual substitutions of clustered arginine residues of the sensor kinase KdpD of Escherichia coli modulate the ratio of kinase to phosphatase activity. J. Biol. Chem., 273: 26400-26415.
Heermann, R., Altendorf, K., Jung, K. (1998) The turgor sensor KdpD of Escherichia coliis a homodimer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1415: 114-124.
1997
Jung, K., Tjaden, B., Altendorf, K. (1997) Purification, reconstitution and characterization of KdpD, the turgor sensor of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 272: 10847-10852.
1996
Puppe, W., Zimmann, P., Jung, K., Lucassen, M., Altendorf, K. (1996) Characterization of truncated forms of the KdpD protein, the sensor kinase of the K+-translocating Kdp system of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 271: 25027-25034.
1995
Jung, K., Jung, H., Colacurcio, P., Kaback, H.R. (1995) Role of glycine residues in the structure and function of lactose permease, an Escherichia coli membrane transport protein. Biochemistry, 34: 1030-1039.
Jung, K., Voss, J., He, M., Hubbell, W.L. and Kaback, H.R. (1995) Engineering a metal binding site within a polytopic membrane protein, the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry, 34: 6272-6277.
Kaback, H.R., Jung, K., Jung, H., Wu, J., Privé, G.G. and Zen, K. (1995) Helix packing in the C-terminal half of lactose permease. in Advances in Cell and Molecular Biology of Membranes and Organelles (R.E. Dalbey, Ed.) 4, pp. 129-144, JAI Press, Inc.
1994
Jung, K., Jung H., Kaback H.R. (1994) Dynamics of lactose permease of Escherichia colidetermined by site-directed fluorescence labeling. Biochemistry, 33: 3980-3985.
Jung, H., Jung, K., Kaback, H.R. (1994) Cysteine-148 of lactose permease of Escherichia coli is a component of a substrate binding site. I. Site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry, 33: 12160-12165.
Roth, S., Jung, K., Jung, H., Hommel, R., Kleber, H.-P. (1994) Crotonobetaine reductase from Escherichia coli - a new inducible enzyme of anaerobic metabolization of L(-)-carnitine. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 65: 63-69.
Kaback, H.R., Frillingos, S., Jung, H., Jung, K., Privé, G.G., Ujwal, M.L., Weitzman, C., Wu, J. and Zen, K. (1994) The lactose permease meets Frankenstein. J. Exp. Biol., 196: 183-195.
1993
Consler, T., Persson, B., Jung, H., Zen, K., Jung, K., Verner, G., Prive, G.G., Kaback, H.R. (1993) Properties and purification of an active biotinylated lactose permease from Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 90: 6934-6938.
Jung, K., Jung, H., Wu, J., Prive, G.G., Kaback, H.R. (1993) Use of site-directed fluorescence labeling to study proximity relationships in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry, 32: 12273-12278.
Jung, H., Jung, K. and Kleber, H.-P. (1993). Synthesis of L-carnitine by microorganisms and enzymes. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol., 50: 21-44.
Kaback, H.R., Jung, K., Jung, H., Wu, J. and Prive, G.G. (1993) What’s new with lactose permease. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr., 25: 627-635.
1990
Jung, H., Jung, K., Kleber, H.-P. (1990) L-Carnitine metabolization and osmotic stress response in Escherichia coli. J. Basic Microbiol., 30: 409-413.
Jung, H., Jung, K., Kleber, H.-P. (1990) L-Carnitine uptake by Escherichia coli. J. Basic Microbiol., 30: 507-514.
1989
Jung, H., Jung, K., Kleber, H.-P. (1989) Purification and properties of carnitine dehydratase from Escherichia coli - a new enzyme of carnitine metabolization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1003: 270-276.
1987
Jung, K., Jung, H., Kleber, H.-P. (1987) Regulation of L-carnitine metabolism in Escherichia coli. J. Basic Microbiol., 27: 131-137.
1985
Jung, K., Kleber, H.-P. (1985) Vorkommen und Regulation der Carnitindehydrogenase in Pseudomonas Spezies. Wiss. Z. Karl-Marx-Univ. Leipzig, Math.-Nat. R. 34, 293-296.
Patents
Jung, H., Jung, K. and Kleber, H.-P. Verfahren zur enzymatischen Synthese von L(-)-Carnitin AP C 12 P / 308 243 6; DD 281 735 A7; AT 26.10.1987, EP 0 320 460 A2
Jung, H., Jung, K., and Kleber, H.P. Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Enzyms AP C 12N / 308 242 8; DD 281 919 A7; AT 26.10.1987
Join the Jung Lab
Contact Kirsten Jung for possibilities to work on exciting projects as Postdoc, PhD student or undergraduate researcher.
Current openings:
We are looking for Master students (master thesis or lab rotations) working in the following areas:
1. Exploring the multi-layered acid resistance network of E. coli. The role of sORFFs.
Reference: Schumacher, K., Gelhausen, R., Backofen, R., Kion-Crosby, W., Barquist, L., Jung, K. (2023) Ribosome profiling reveals the fine-tuned response of Escherichia coli to acid stress. mSystems, Nov 1:e0103723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01037-23
Please send your complete application in English as a single PDF (CV, motivation statement and research experience, record of study, certificates) to Prof. Dr. Kirsten Jung jung@lmu.de).
2. Exploring the multi-layered acid resistance network of E. coli. The molecular mechanism of the acid-sensor AdiY.
Reference: Brameyer S, Schumacher K, Kuppermann S, Jung K (2022) Division of labor and collective functionality in Escherichia coli under acid stress. Commun Biol, 5:327. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03281-4
Please send your complete application in English as a single PDF (CV, motivation statement and research experience, record of study, certificates) to Prof. Dr. Kirsten Jung jung@lmu.de).
3. Finding of new antibiotic targets in stationary phase cells.
Single cell studies, microscopy, reporter strains.
Please send your complete application in English as a single PDF (CV, motivation statement and research experience, record of study, certificates) to Prof. Dr. Kirsten Jung jung@lmu.de).
4. New insights into the transcriptome of Escherichia coli by third generation sequencing.
Third generation sequencing methods allow direct sequencing of RNA and DNA molecules without any bias or PCR. This approach helps tremendously in the identification and description of RNA molecules such as novel antisense RNAs, novel transcription start sites (TSSs), transcription termination sites, and operons. We have generated several datasets that require in-depth bioinformatics analysis.
Requirements:
The candidate should be enrolled in a Master Program in Bioinformatics (or equivalent). The candidate should be highly motivated and determined, with a strong interest in genomics and transcriptomics and the application of interdisciplinary approaches.
Qualifications:
Experience in genome/transcriptome analysis and bioinformatics methods is required.
Please send your complete application in English as a single PDF (CV, motivation statement and research experience, record of study, certificates) to Prof. Dr. Kirsten Jung (jung@lmu.de). In case of specific questions please contact Dr. Sebastian Riquelme-Barrios (S.Riquelme@biologie.uni-muenchen.de).
Duration: 6 months
5. Conformational changes underlying transcriptional regulation of Lys-R type regulators.
The LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) family is one of the largest groups of bacterial transcription regulators, which are highly conserved among prokaryotes.[1] They regulate a wide spectrum of cellular functions, as for example, oxidative stress response, virulence, motility and quorum sensing. LTTRs are unique in the sense that they function both as repressors and activators of single operonic genes. LTTRs show a conserved structure with an N-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD) with a winged helix-turn-helix motif.[2] Effector binding takes place at the C-terminal domain (EBD), which is linked to the DBD via a linker helix (see Figure on the left). The proteins form dimers and tetramers in solution, but are functionally active as tetramers when bound to dsDNA[3]. On DNA they induce bending, which in turn facilitates recruitment of RNA polymerase. While there are some structures and structural models of LTTRs available (including their complexes with dsDNA), the concrete mechanism by which LTTRs use conformational changes, i.e., in the EBD, their quaternary structure or in the degree of DNA-bending, remain poorly understood.
The goal of this project is to investigate effector-induced conformational changes of an LTTR model system in the EBD (in its DNA-bound and unbound state), and to observe the degree of DNA bending under different conditions by biophysical techniques. ArgP from E. coli is a typical member of the LTTR family and controls the transcription of the argO gene encoding an exporter for arginine and canavanine to maintain an optimal ratio of intracellular arginine to lysine. We produced cysteine variants of ArgP that can be labelled with two fluorophores to monitor the conformational states of the EBDs via single-molecule FRET, smFRET (see Figure on the right). We further obtained fluorophore-labelled promoter DNA that will serve as a bending sensor when it interacts with wildtype ArgP. In the project, you will use established protocols to obtain the relevant ArgP variants, introduce fluorescence labels and perform biophysical assays. Biochemical properties of the system will be characterized by ligand-affinity measurements using calorimetry and microscale thermophoresis with the effectors arginine and lysine. Structural characterization of ArgP and its dsDNA complexes will be conduced via smFRET.[4]
The work will be performed in the section “Microbiology” in collaboration between the groups of Kirsten Jung (Molecular Microbiology, jung@lmu.de) and Thorben Cordes (Physical and Synthetic Biology, cordes@bio.lmu.de). It is ideally suited for motivated students with an interest and background in microbiology, biochemistry, structural biology and biophysics.
References:
[1] Schell, M. A., Molecular Biology of the LysR Family of Transcriptional Regulators. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 47 (1993), pages 597–626.
[2] Zhou, X. et al., Crystal Structure of ArgP from Mycobacterium tuberculosis Confirms Two Distinct Conformations of Full-length LysR Transcriptional Regulators and Reveals Its Function in DNA Binding and Transcriptional Regulation. Journal of Molecular Biology 396 (2010), pages 1012–1024.
[3] Maddocks, S. E. et al., Structure and function of the LysR-type transcriptional regulator (LTTR) family proteins. Microbiology 154 (2008), pages 3609–3623.
[4] Lerner, E. et al., Toward dynamic structural biology: Two decades of single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer. Science 359 (2018), eaan1133